Common Applications

Stamping Presses
In stamping operations, both the press and the dies require lubrication to ensure quality production. Presses typically require grease in the bearings and at the metal-to-metal sliding interfaces. While lubricants can be applied manually, automatic systems are more consistent and dependable.

Robotic Welding Systems
Bearings, gears, and joints within robotic welding systems require proper lubrication to minimize wear, reduce drag, and prevent heat build-up. Collectively, these help the robot deliver the repeatability required while achieving productivity and quality goals.
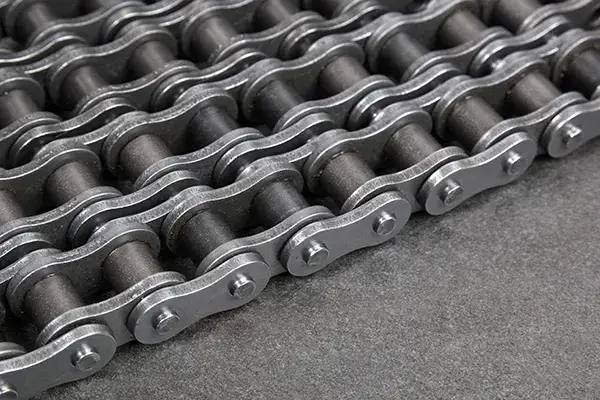

Conveyor Systems & Chain Drives
Chains benefit from drip or spray lubrication systems, which lower friction, saving energy and extending life, while bearings are often grease-lubricated to exclude contaminants from metal-to-metal interfaces.
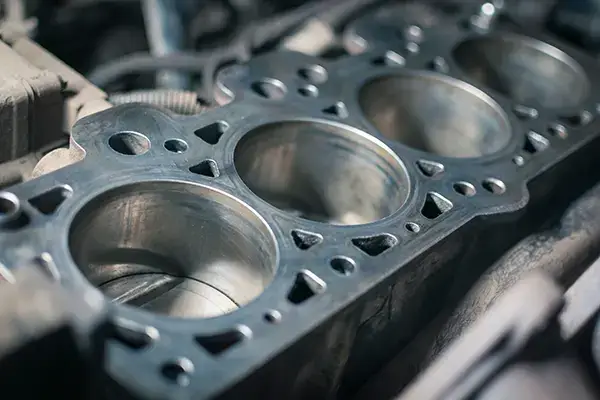

Engine Block & Cylinder Machines
Using the right lubricants for engine blocks and cylinder machines drives out waste and ensures performance and durability. Minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) helps optimize cutting conditions and increase productivity by simplifying chip disposal and preventing surface corrosion.
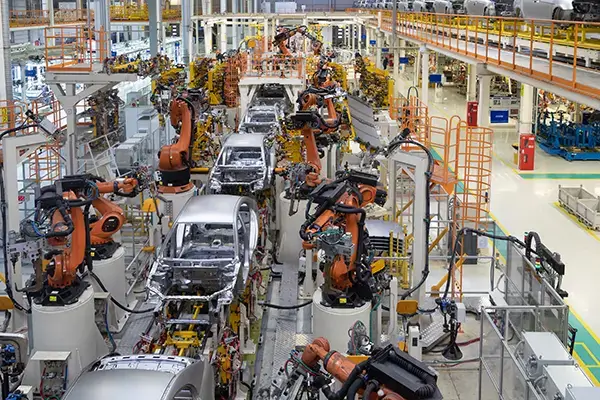

Body Assembly Lines
Unplanned downtime on these hugely complex systems is extremely costly. Precise delivery of the correct lubricants minimizes component wear while protecting against corrosion. Additional benefits include lower friction, enhanced movement precision, and reduced heat generation.
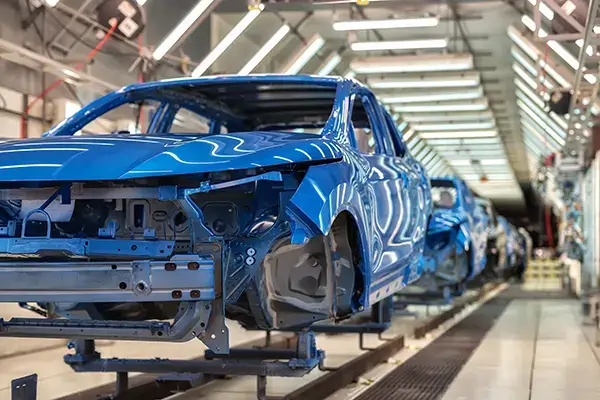

Paint Shop & Final Assembly Equipment
In addition to stable, consistent motion, lubrication in the paint shop helps exclude contaminants from metal-to-metal interfaces. By reducing wear rates, this extends equipment life and helps organizations meet ROI goals for their assets.